Italy
| Author:Laxman Burdak, IFS (R) |
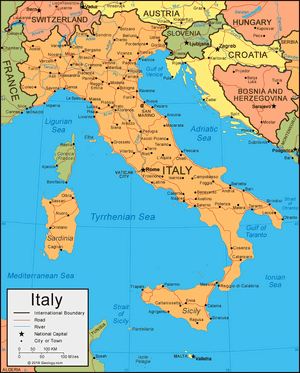

Italy (इटली) is a Southern European country.
Variants
- Italy (Anabasis by Arrian, p. 152, 399.)
Location
It comprises the Italian peninsula, the Po River valley, and two large islands in the Mediterranean Sea, Sicily and Sardinia, and shares its northern alpine boundary with France, Switzerland, Austria, and Slovenia. The country also shares a sea border with Croatia, and France.
Etymology
The assumptions on the etymology of the name "Italia" are very numerous and the corpus of the solutions proposed by historians and linguists is very wide.[1] According to one of the more common explanations, the term Italia, from Latin: Italia,[2] was borrowed through Greek from the Oscan Víteliú, meaning "land of young cattle" (cf. Lat vitulus "calf", Umb vitlo "calf").[3] The bull was a symbol of the southern Italian tribes and was often depicted goring the Roman wolf as a defiant symbol of free Italy during the Social War.
Jats in Italy

Ram Sarup Joon[4] writes that .... In 500 BC, Jats took part in the civil war in Italy. When the hunters invaded Italy, the Jats defeated them on the battlefield of Nester. As a reward the ruler of Italy permitted them to occupy the Danube basin called Balkans now. After four years, differences arose between the Jats and king Theodius of Italy,
History of the Jats, End of Page-41
who attacked the Jats. The Jats were victorious and occupied Asia Minor. Then they attacked Rome and after defeating the famous military commander Allers, occupied the south Eastern portion of Italy. Theodius gave his daughter in marriage to the Jat leader. The Jats vacated Italy, advanced into and settled in Spain and Portugal.
In 490 BC, there was another battle after which Jats occupied the whole of Italy and ruled there for 65 years upto 425 BC. During this period Italy made a great measure of progress.
After the death of the great Jat leader Totila, the Jat power declined and they were driven out of Italy. Soon after, the Arabs drove the Jats out of Spain and Portugal. Consequently Jats were so weakened and scattered that they ceased to exist as a recognised group in this area.
Rome, the capital of Italy, was for centuries a political and religious centre of Western civilisation as the capital of the Roman Empire and site of the Holy See. After the decline of the Roman Empire, Italy endured numerous invasions by foreign peoples, from Germanic tribes such as the Lombards and Ostrogoths, to the Byzantines and later, the Normans, among others. Centuries later, Italy became the birthplace of Maritime republics and the Renaissance, an immensely fruitful intellectual movement that would prove to be integral in shaping the subsequent course of European thought.
Migrations from Indian to north western countries
Hukum Singh Panwar (Pauria)[5] writes that We may now cite at some length from Pococke[6] who has traced Indian migrations to all corners of the world solely through linguistic similarities. This extreme reliance on phonetic similarities seems to weaken his argument, but there is ample support, from other disciplines, techniques and lines of investigation, for his claims. Further, the large body of data, he has massed together cannot be brushed away lightly. When supported by other evidence, his thesis becomes incontrovertible. According to Pococke a great number of adventurous preux chevalier tribes from India migrated to Spain, Italy, Greece, Asia Minor,Persia, Colchis, Armenia and the Caucasus region, all of which provide distinct and startling evidence of Indian colonization in great profusio. We have tried (Appendix No.6) to pinpoint the Indian names and places of the origin of the migrated tribes as well as the altered forms of their names in their new settlements in other countries. The appendix indicating all this, is by no means, exhaustive. It may not be unnecessary here to point out that in some countries the presence of Indian tribes can be construed by their names, though distorted, while, in others their identity can be traced by place names in these transformed phonemic nomenclatures. All the more significant is the fact that almost all the tribes are considered Saca-Getae (Jats) or Scythians by the learned scholar[7].(cf. Appendix No.6).
Pococke[8] believes that the major migrations took place from India as a result of internecine wars and religious persecutions in which the Buddhists had been the main victims.
To these may be added the Parasurama-Haihayas (Scythians) wars, Sagar's war against Haihayas and their allies (Sakas, Parthas,Pahlavas etc) the Dasarajna Wars, the Rama-Ravana Yudha, the Mahabharata war. Pococke lays special stress on the virulent religious strife for a long time between the Brahmins and the Buddhists for supremacy, leading to Brahmanic victory and the gigantic expulsion of the Buddhists. Pococke claims[9] that this was the most crucial event which compelled migrations and
The Jats:Their Origin, Antiquity and Migrations:End of page 307
banishment of the vanquished to the north-western countries. The Saga of the Kurus and Pandus, though ostensibly political was in reality, as Pococke[10] contends, a struggle between the Brahminical and the Buddhistic parties. Profound night clouds this portion on Indian history. What Pococke regards as clear is that the emigrants coasted along the shores of Mekran, traversed the mouth of Persian Gulf. Adhering to the sea-board of Oman, Hadramant and Yemen (the Eastern Arabia), they sailed up the Red Sea, and ascending the mighty stream - the Nile - that fertilizes a land of wonders, founded the kingdoms of Egypt, Nubia, Abyssinia[11] and Ethiopia. Fhilostratus, Julius Africanus, Eusebius and Syncellus, the Greek writers[12] assert that the Ethiopians were originally an Indian race, emigrated from the river Indus and settled in the vicinity of Egypt. This assertion cannot be dismissed lightly.
German Effect on Jutland
Mangal Sen Jindal[13] writes....German Effect on Jutland: "The Danish language belongs to the East Scandinavian group of Germanic languages. The national religion, to which the bulk of the population belongs, is Lutheran Evangilical. The only non-Danish minority is a German element." [14]
"Migrations and invasions from the continent early flowed across the open borderland of Jutland. By the same route came culture currents from Western Europe and Germany, which Denmark received and adapted to her own genius. But even in the Iron Age, with its vigorous economic and social development, Danish tribes trekked across Europe towards Germany and Italy and sailed their vessels to Britain. This first great expansion was followed from about 500-600 A.D. by another, which along with Norwegian Viking raids to the west and Swedish to the east, continued for several centuries and culminated around 900-1000 A. D." [15]
"The Juts of Jutland expanded to Cologne, Paris, Nantes, Spain, Camargue Luna (Italy) Greece, Constantinopel, Novgorod (USSR), Kiev, Itil and Semender etc., all prior to 1000 A.D." ...... Denmark Official Handbook, page 71. Refer to the map in this Chapter dealing with migration and immigration of Jats.
"Towards the end of eighth century A. D. Viking seafarers began a series of raids from the North. The roads marked the start of the Viking rea, a span of some 250 years when a tremendous outpouring of energy carried man of the North to such far flung places as Greenland and Bagdad.
History of Origin of Some Clans in India:End of p.92
During the Viking Era these people colonized parts of England and France and all of Sicily. They established the first Russian kingdom. They traded slanes and furs for Chinese silks and Arab Silver in the markets of Bagdad." Who discovered America by Patricia Lauber published by Randon House, New York-pages 79 and 80.
The viking expansion had important consequences for development in Denmark itself. Riches, slaves and foreign culture were imported; at the same time those who stayed at home cleared large tracts of forest and built many new villages. Large farmers became estate-owners. " [16]
"The new influence flowing from the South reached Denmark chiefly through North Germany. A culture which flourished among enterprising merchants and artisans of the Hanseatic towns exerted a profound influence, also linguistically, on Denmark." [17]
"Of the Judicial system before 1200 there is only very incomplete knowledge, but by about 1200 A. D. there were three separate areas of jurisdiction, each with its own law; The Jutland code, the Zealand code and the Scanean code. The last-named gradually lost their importance and were superseded by the Jutland area." [18]
It is difficult to study religious history of Jutland of prior to 826 A.D. when "Christianity was introduced in 826 by the mission of the Benedictine monk Ansgar, from northern France. But it was not adopted until 960....When the king had himself baptized and ordered the religion's introduction." [19]
The only non-Danish minority is a German element in South Jutland numbering about 40,000 or less than 0.8 percent of the population. Big industrial expansion has caused a large immigration of foreign workers, totaling 54,000 (1972).
प्राचीनकाल में यूरोप देश
दलीप सिंह अहलावत[20] लिखते हैं: यूरोप देश - इस देश को प्राचीनकाल में कारुपथ तथा अङ्गदियापुरी कहते थे, जिसको श्रीमान् महाराज रामचन्द्र जी के आज्ञानुसार लक्ष्मण जी ने एक वर्ष यूरोप में रहकर अपने ज्येष्ठ पुत्र अंगद के लिए आबाद किया था जो कि द्वापर में हरिवर्ष तथा अंगदेश और अब हंगरी आदि नामों से प्रसिद्ध है। अंगदियापुरी के दक्षिणी भाग में रूम सागर और अटलांटिक सागर के किनारे-किनारे अफ्रीका निवासी हब्शी आदि राक्षस जातियों के आक्रमण रोकने के लिए लक्ष्मण जी ने वीर सैनिकों की छावनियां आवर्त्त कीं। जिसको अब ऑस्ट्रिया कहते हैं। उत्तरी भाग में ब्रह्मपुरी बसाई जिसको अब जर्मनी कहते हैं। दोनों भागों के मध्य लक्ष्मण जी ने अपना हैडक्वार्टर बनाया जिसको अब लक्षमबर्ग कहते हैं। उसी के पास श्री रामचन्द्र जी के खानदानी नाम नारायण से नारायण मंडी आबाद हुई जिसको अब नॉरमण्डी कहते हैं। नॉरमण्डी के निकट एक दूसरे से मिले हुए द्वीप अंगलेशी नाम से आवर्त्त हुए जिसको पहले ऐंग्लेसी कहते थे और अब इंग्लैण्ड कहते हैं।
द्वापर के अन्त में अंगदियापुरी देश, अंगदेश के नाम से प्रसिद्ध हुआ, जिसका राज्य सम्राट् दुर्योधन ने अपने मित्र राजा कर्ण को दे दिया था। करीब-करीब यूरोप के समस्त देशों का राज्य शासन आज तक महात्मा अंगद के उत्तराधिकारी अंगवंशीय तथा अंगलेशों के हाथ में है, जो कि ऐंग्लो, एंग्लोसेक्शन, ऐंग्लेसी, इंगलिश, इंगेरियन्स आदि नामों से प्रसिद्ध है और जर्मनी में आज तक संस्कृत भाषा का आदर तथा वेदों के स्वाध्याय का प्रचार है। (पृ० 1-3)।
यूरोप अपभ्रंश है युवरोप का। युव-युवराज, रोप-आरोप किया हुआ। तात्पर्य है उस देश से, जो लक्ष्मण जी के ज्येष्ठपुत्र अङ्गद के लिए आवर्त्त किया गया था। यूरोप के निवासी यूरोपियन्स कहलाते हैं। यूरोपियन्स बहुवचन है यूरोपियन का। यूरोपियन विशेषण है यूरोपी का। यूरोपी अपभ्रंश है युवरोपी का। तात्पर्य है उन लोगों से जो यूरोप देश में युवराज अङ्गद के साथ भेजे और बसाए गये थे। (पृ० 4)
कारुपथ यौगिक शब्द है कारु + पथ का। कारु = कारो, पथ = रास्ता। तात्पर्य है उस देश से जो भूमध्य रेखा से बहुत दूर कार्पेथियन पर्वत (Carpathian Mts.) के चारों ओर ऑस्ट्रिया, हंगरी, जर्मनी, इंग्लैण्ड, लक्षमबर्ग, नॉरमण्डी आदि नामों से फैला हुआ है। जैसे एशिया में हिमालय पर्वतमाला है, इसी तरह यूरोप में कार्पेथियन पर्वतमाला है।
इससे सिद्ध हुआ कि श्री रामचन्द्र जी के समय तक वीरान यूरोप देश कारुपथ देश कहलाता था। उसके आबाद करने पर युवरोप, अङ्गदियापुरी तथा अङ्गदेश के नाम से प्रसिद्ध हुआ और ग्रेट ब्रिटेन, आयरलैण्ड, ऑस्ट्रिया, हंगरी, जर्मनी, लक्षमबर्ग, नॉरमण्डी, फ्रांस, बेल्जियम, हालैण्ड, डेनमार्क, स्विट्जरलैंड, इटली, पोलैंड आदि अङ्गदियापुरी के प्रान्तमात्र महात्मा अङ्गद के क्षेत्र शासन के आधारी किये गये थे। (पृ० 4-5)
नोट - महाभारतकाल में यूरोप को ‘हरिवर्ष’ कहते हैं। हरि कहते हैं बन्दर को। उस देश में अब भी रक्तमुख अर्थात् वानर के समान भूरे नेत्र वाले होते हैं। ‘यूरोप’ को संस्कृत में ‘हरिवर्ष’ कहते थे। [21]
रोम की ओर जाट
ठाकुर देशराज[22] ने लिखा है: रोम की ओर जाट (गाथ) लोगों ने 250 ई. से बढ़ना शुरू किया था यद्यपि जाट रोम से ईसवी सन् से पूर्व कई शताब्दी से परिचित थे और उन्होंने डेरियस के साथ ईसा से 500 वर्ष पहले रोम के पड़ोसी यूनान पर आक्रमण किया था। सिकन्दर का भी उन्होंने फारिस के मैदानों में मुकाबला किया था। रोम में कई बार में जाकर इन्होंने बस्तियां आबाद कर ली थीं। रोम उस मसय गृहकलह में भी फंसा हुआ था। वे उत्तम सैनिक तो थे ही, इसलिए आक्रमणों से पहले रोम की सेना में स्थान पा चुके थे।
374 ई. में मध्य-यूरोप के लोगों पर ऐशिया से आई हुई, बर्बर जाति के हूणों ने आक्रमण किया। नीस्टर नदी के पास भयंकर युद्ध के बाद जाटों को आगे बढ़ने को विवश होना पड़ा। रोम सम्राट वैलिन्स की सहमति से उन्होंने बालकन प्रायद्वीप में डेन्यूब नदी के किनारे अपना जनपद स्थापित किया और भारी संख्या में वहा बस गये। कुछ ही दिन के बाद रोम के सम्राट ने उन्हें निकालने के लिए छेड़-छाड़ आरम्भ कर दी। भला परिश्रम-पूर्वक आबाद किये हुए देश को वे कैसे छोड़ सकते थे। कशमकश यहां तक बढ़ी कि पूर्व मित्रता के भाव नष्ट हो गये और युद्ध छिड़ गया।
378 में सम्राट वेलिन्स ने रोमनों की एक बड़ी सेना के साथ गाथों (जाटों) पर
जाट इतिहास:ठाकुर देशराज,पृष्ठान्त-189
आक्रमण कर दिया। बड़ा घमासान युद्ध हुआ। किन्तु एड्रियानोपल नगर के पास गाथों के एक घुड़सवार दल ने रोमन लोगों को करारी परास्त दी। रोमन भाग खड़े हुए। सम्राट सख्त घायल हुआ और युद्ध-भूमि में ही मारा गया। गाथों के नेता की भी इसी समय मृत्य हो गई। साथ ही प्लेग भी फैल गया। इससे वह अपनी विजय पर हर्ष उत्सव न मना सके।
सम्राट बेलिन्स के उत्तराधिकारी सम्राट थियोडोसियस ने भी शासन-भार हाथ में आते ही जाटों पर चढ़ाई की, किन्तु अन्त में उसे गाथों (जाटों) से सन्धि करनी पड़ी। इस सन्धि के अनुसार थ्रेस और एशियाई माइनर में बहुत सी भूमि उसे उनको देनी पड़ी। जाटों ने भी बदले में रोम को चालीस हजार सेना की सहायता देना स्वीकार किया। यद्यपि यह सेना रोम के अधीन समझी जाती थी, किन्तु उसके अफसर जाट ही थे। इससे सम्राट दिल में शंकित भी रहता था, पर जाटों ने ईमानदारीपूर्वक सन्धि को निभाया।
395 ई. में सम्राट थियोडोसियस मर गया। उसने अपने दो पुत्रों को अपना राज्य बांट दिया था। बड़ा पुत्र आर्केडियस पूर्वी भाग का मालिक था। राजधानी उसकी कॉस्टेन्टाइन थी। दूसरा पुत्र होनोरियस पच्छिमी भाग का अधिकारी हुआ और मिलन में राजधानी रखी। इस समय गाथ लोगों से दोनों सम्राटों का सम्बन्ध हो गया था। गाथों का प्रसिद्ध नेता एलरिक इस समय अधिक प्रसिद्ध था। उसने पहले तो रोम के पूर्वी भाग को जाटों से अधिकृत करने के अभिप्राय से चढ़ाई की किन्तु कान्स्टेण्टीनोपुल की सुदृढ़ दीवारों को उसकी सेना न भेद सकी। अतः उसने मिलन पर चढ़ाई की। होनोरियस सम्राट के बंडाल सेनापति स्टिलाइको से मुकाबला हुआ। विशेष तैयारी न होने के कारण एलरिक की हार हुई। किन्तु एलरिक हताश होने वाला व्यक्ति न था। सन् 408 ई. में दुबारा चढ़ाई कर दी। बादशाह ने कुछ वायदे उसके साथ ऐसे किये, जिससे उसे घेरा उठा लेना पड़ा। किन्तु बादशाह ने वायदे को पूरा न किया। इसलिये एलरिक ने तीसरी बार इटली को फिर घेर लिया। रोमन लोग हार गए, शहर पर जाटों का अधिकार हो गया। एलरिक ने इटली के दक्षिण भाग को भी विजय करने की इच्छा से चढ़ाई की, किन्तु वहां वह बीमार होकर मर गया। यद्यपि गाथ नेताविहीन हो गए थे, फिर भी दृढ़ रहे, और औटाल्फस (अतुलसैन) को अपना राजा बनाया। रोम का पूर्वी भाग ले सम्राट थियोडोसियस गाथों (जाटों) से बहुत डरा हुआ था। उसने गाथों से निश्चिन्त होनें के लिये यही उत्तम समझा कि अपनी लड़की की शादी (अटाल्फस) के साथ कर दी| इस तरह से जाट और रोमन्स लोगों का रक्त सम्बन्ध स्थापित हो गया।
यह रोमन लड़की बड़ी स्वजाति-भक्त थी, यद्यपि वह जाटों के घर में आ गई थी, किन्तु चाहती यही थी कि रोमन लोग जाटों से निर्भय हो जायें, इसलिये उसने गाथों को सलाह दी कि इटली से बाहर अपना साम्राज्य स्थापित करें।
जाट इतिहास:ठाकुर देशराज,पृष्ठान्त-190
उसकी सलाह के अनुसार गाथों (जाटों) ने स्पेन और गाल के बीच अपना साम्राज्य स्थापित किया जो 300 वर्ष तक कायम रहा।
सन् 446 ई. में हूणों ने एटिला की अध्यक्षता में रोम का ध्वंश करते हुए गाल पर आक्रमण किया जो कि रोमन और गाथों का सम्मिलित प्रदेश था। इस समय रोमन और गाथों ने एटिला की सम्मिलित शक्ति के साथ मुकाबला किया, हूण हार गए और एटिला को निराश होना पड़ा।
यूरोप में जाटों (गाथों) को ट्यूटानिक जाति में (दल) गिना गया है। हमारी समझ में प्रजातंत्री अथवा शक्ति-सम्पन्न होने के कारण उन्हें यह नाम दिया गया है। तांत्रिक शब्द से भी ट्यूटानिक बन सकता है, इन ट्यूटानिक लोगों मे गाथ, फ्रेंक, डेन, ऐंगल तथा सैक्सन आदि हैं।
यह ट्यूटांनिक जातियां स्कंधनाभ और राइन प्रदेश मे बसी हुई बताई गई हैं। यहां से उठकार काला सागर और डेन्यूब में बसने वाले लोगों को गाथ (जाट) कहा गया है।
इन लोगों को प्रजातंत्री बताया गया है। स्थानीय झगड़ों का फैसला नगर के मुखिया लोग ही इनके यहां करते थे, ऐसा यूरोप वालों का कथन है। ग्रामों में पंचायतों और प्रान्त में जनसभा के द्वारा शासन करते थे। इनकी सभाओं में सरदार और नागरिक की राय का मूल्य बराबर था। इनके युवक लोग किसी सरदार के पास रहकर सैनिक-शिक्षा प्राप्त करते थे, इससे सरदारों और युवकों में घनिष्ठ सम्बन्ध रहता था। प्रायः एक-एक योद्धा के पास बीसियों युवक होते थे।
धर्म में यह प्रकृति के उपासक थे, ऐसा यूरोप वालों का अनुमान है। वे कहते हैं, ये वृक्षों और गुफाओं की भी पूजा करते थे।1 इनमें कोई अलग पुजारी-दल न था। प्रायः सभी लोग चौपाये पालते थे। खेती करना इन्हें बहुत पसन्द था और शिकार भी खेलते थे। ये लोग सटी हुई बस्तियां पसन्द करते थे। नगर दूर-दूर और खुले मैदान में बनाते थे। इस कारण स्वस्थ और बलवान रहते थे। इनके लम्बे कद, उज्जवल रंग, बलवान शरीर और सुर्ख चेहरे को देखकर रोमवालों पर बहुत प्रभाव पड़ा। लड़ने को तो ये अपना पेशा समझते थे, सत्यप्रियता के लिए बहुत प्रसिद्ध थे।
इटली के जाट पूर्वी गाथ कहलाते थे और स्पेन की ओर बसे हुए पश्चिमी गाथ के नाम से रोमन लोगों द्वारा पुकारे जाते थे। 489 ई. में पूर्वी गाथों के सरदार थियोडेरिक (देवदारूक) ने इटली पर आक्रमण किया। 4 वर्ष की निरन्तर लड़ाई के बाद इटली के तत्कालीन सम्राट औडोवकर ने इटली का आधा राज्य
- 1.ये ही बातें तो भारत के जाटों में हैं, वे पीपल और खेजड़ी को पूजते हैं। पुजारियों का दल तो भला उनके साथ विदेश जाता ही क्यों?
जाट इतिहास:ठाकुर देशराज,पृष्ठान्त-191
देकर गाथों से सन्धि कर ली। थोड़े ही दिन बाद थियोडोरिक (देवदारूक) ने औडोवकर को मरवाकर सारी इटली पर गाथों का अधिकार जमा दिया। रोमन लोगों के साथ उसने सख्त व्यवहार न करके इन्हें इतना सुख दिया कि वे यह कहने लग गये कि खेद है कि
- ‘जाट इससे पूर्व ही हमारे यहां क्यों न आये।’
बड़े-बड़े पदों पर रोमनों को नियुक्त किया। नगर, सड़क, बाग-बगीचे, बनाए तथा सड़क और नहरों की मरम्मत कराई । कृषि और उद्योग-धन्धों की वृद्धि के लिए प्रोत्साहन दिया। तेतीस वर्ष के अपने राज्य-काल में उसने इटली को कुबेरपुरी बना दिया। इसके अलावा पड़ोसी जर्मनी से विवाह सम्बन्ध करके सम्राज्य की नींव को और भी मजबूत किया। इतने अच्छे जाट सरदार की 526 ई. में मृत्यु हो गई। इससे जाट (गाथ) और रोमन सभी को बड़ा दुःख हुआ। इटली के पूर्वी गाथों का यह सबसे बड़ा और लोकप्रिय सरदार था। उसके बाद सन् 553 तक उसके वंशजों के हाथ में इटली का राज्य रहा। इसी सन् में उनके हाथ से रोमन सम्राट जस्टिनियन ने इटली का राज्य छीन लिया।
पश्चिम के जाट लोगों ने दक्षिणी गाल और स्पेन पर अधिकार कर लिया था, यह पीछे लिखा जा चुका है। आठवी शताब्दी तक उन्होंने वहां बड़ी निर्भयता और सफलता के साथ शासन किया। बीच में फ्रेंक राजाओं से उन्हें युद्ध करने पड़े थे और हानि भी रही थी। किन्तु मेरेसिन लोगों ने आठवीं शताब्दी के मध्य में प्रबल आक्रमणों से उनके राज्य का अन्त कर दिया। इस तरह रोम से जाटों का साम्राज्य जाता रहा। किन्तु उन्होंने आशा को न छोड़ा इस समय के स्पेनिश में केल्ट, रोमन गोथ तथा मूर कई जातियों का मेल है। जस्टिनियन ने गाथों से इटली के पूर्वी-पच्छिमी हिस्से की जीतने के बाद अन्य देशों पर भी चढ़ाइयां कीं, साथ ही बहुत सी इमारतें बनवा डालीं, जिससे उसका खजाना खाली हो गया। प्रजा में आर्थिक कष्ट बढ़ जाने से लोग जाटों के राज्य की याद करने लगे। इस असन्तोष से लाभ उठाने का गाथों ने फिर एक बार प्रयत्न किया और टोटिला (तोतिला) नाम से एक वीर सरदार की अध्यक्षता में इटली पर आक्रमण किया। टोटिला बड़ा न्यायी और वीर था, 538 ई. में उसने कई लड़ाइयों के बाद इटली पर फिर जाटों का अधिकार कर दिया। 14 वर्ष तक गाथ लोगों का सितारा इटली में चमकता रहा। 552 ई. में उनके विरूद्ध रोमनों ने फिर से तलवार उठाई। टोटिला बड़ी बहादुरी के साथ लड़ा, उसके बहुत से घाव आये जिनके कारण थोड़े ही दिनों में वह इस संसार से चल बसा। गाथ लोग फिर भी कई बार रोमनों से लड़े, किन्तु बार-बार के युद्धों के कारण उन्हें इटली छोड़ना पड़ा। और आल्पस को पार कर के पश्चिमी जाटों में जा मिले। इटली में उनका कुछ भी अस्तित्व न रह गया ।
जाट इतिहास:ठाकुर देशराज,पृष्ठान्त-192
उस समय यूरोप में एक नया धर्म खड़ा हुआ था जिसका नाम महात्मा ‘यीशु’ के नाम पर ईसाई धर्म था। इस धर्म के प्रति यीशु को फांसी के पश्चात् लोगों के हृदय में सहानुभूति पैदा हो गई थी। इसके सिद्धान्त भी बौद्ध-धर्म से मिलते-जुलते थे। इसलिये गाथों पर भी जो कि अपनी मातृ-भूमि भारत से सदियों तक दूर हो चुके थे, ईसाई धर्म का प्रभाव पड़ गया और वे बारहवीं सदी तक सबके सब ईसाई हो गये। यदि भारतीय उपदेशक पौराणिक-धर्म की आज्ञा के प्रतिकूल विदेश-यात्रा करते रहते, तो बहुत सम्भव था, कि भारत से गई हुई जाट, कट्टी, सुऐवी, स्लाव, जातियां ईसाई न हुई होतीं। यूरोप के इतिहास में लिखा हुआ है कि गाथ तथा बण्डाल पहले आर्यन मत के अनुयायी थे।
नौवीं सदी तक गाथ, बरगंडी आदि जातियां अपनी पुरानी भाषा को भी भूल गई थीं। अपराध की जांच के लिए वे अग्नि-परीक्षा और जल-परीक्षा लिया करते थे। गर्म तवे अथवा जल में हाथ डलवा कर, अपराध जानने की उनमे वैसी ही प्रथा थी, जैसी कि भारत में थी।
जात इतिहास
डॉ रणजीतसिंह[23] के अनुसार ... देशराज[24] अपने इतिहास में लिखते हैं- "उनका (जाटों का) विस्तार उत्तर में जगजार्टिस और पश्चिम में ईरान की खाड़ी तक हो गया था। ईरान के डेरियस के अलावा अपने नेताओं के साथ उन्होंने यूनान को पहले ही देख लिया था। समय पाकर तथा अधिक संख्या एवं अन्य परिस्थितियों से वे आगे की ओर बढ़े और रोम तथा इटली में पूर्व की ओर से आक्रमण करने लगे। उधर मध्य एशिया में हूणों का प्रथम उपद्रव खड़ा हुआ तब जगजार्टिस के किनारे पर बसे हुए जाट लोगों का कुछ भाग नए और हरे-भरे देशों की खोज के लिए यूराल पर्वत को पार कर गया और जर्मनी में जा बसा। उससे भी अधिक उत्साही लोगों को वहां पहुंचा दिया जहां से आगे थल न था अर्थात जमीन का खात्मा हो गया था, वह देश था स्कंधनाभ अथवा स्कैंडिनेविया।"
References
- ↑ Alberto Manco, Italia. Disegno storico-linguistico, 2009, Napoli, L'Orientale, ISBN 978-88-95044-62-0
- ↑ OLD, p. 974: "first syll. naturally short (cf. Quint.Inst.1.5.18), and so scanned in Lucil.825, but in dactylic verse lengthened metri gratia."
- ↑ J.P. Mallory and D.Q. Adams, Encyclopedia of Indo-European Culture (London: Fitzroy and Dearborn, 1997), 24.
- ↑ Ram Sarup Joon: History of the Jats/Chapter III, p.41
- ↑ The Jats:Their Origin, Antiquity and Migrations/The identification of the Jats, pp.307-308
- ↑ Pococke, E; India in Greece, Indian Reprint, 1972, p. 32, 47, 134.
- ↑ Ibid., pp.38, 51ff, 63, 70, 124, 148, 159, 178, 195, 205, 229, 242, 251, 255,300.
- ↑ For further study please cf. C. Wordsworth, D.O., 'Greece, Pictorial and Descriptive; Grote, His. of Greece; Niebuh" His. of Rome; Troyer, Ramayana; Tod, Ann; Is and Antiquities of Rajasthan; Ency. Metropolitania; Smith, Muth. Lex., vol.I Homer, Odessey, Iliad; Asiatic Researches; Mure, His. of Greek Literatura, . Vol.I; Strabo's Geographia; Wilson, skt. Les.; Kruse, Hellas; Smith, Dic. of Astiq.; Hamilton E, Ind. Gaz., Vol.I; Thoronton, Geog. of Ph.; Thirliwall, His. of Greece; Thueydide, Genesis and App. No. XX in Pococke's Ind. in Greece
- ↑ Ibid., Chs VI-XV
- ↑ Ibid., p. 300. Dr. Buddha Prakash describes the Epic war as the 'Saga of the Sakas'.
- ↑ Ibid., p.43
- ↑ Ibid., p. 205.
- ↑ History of Origin of Some Clans in India/Jat From Jutland/German Effect on Jutland, pp. 92-93
- ↑ Denmark Official Handbook, page 53.
- ↑ Denmark Official Handbook, page 70.
- ↑ Page 72 of Denmark O. H. Book.
- ↑ Page 110 of Denmark O. H. Book.
- ↑ Page 255 of Denmark O.H. Book.
- ↑ Page 239 of Denmark O. H. Book.
- ↑ Jat History Dalip Singh Ahlawat/Chapter IV,p.339-340
- ↑ (सत्यार्थप्रकाश दशम समुल्लास पृ० 173)
- ↑ Jat History Thakur Deshraj/Chapter VI, pp.189-192
- ↑ Jat Itihas By Dr Ranjit Singh/1.Jaton Ka Vistar,p.4
- ↑ देशराज, जाट इतिहास, पृष्ठ 169-71